Cloud-based
Neuroimaging
Cloud platform that converts MRI scans into interpretable maps of brain abnormalities with automated lesion detection.

About EpiVis
We are a team from Newcastle University, developing advanced neuroimaging tools to transform neurological care.
Our cloud-based platform converts standard MRI scans into fast, interpretable maps of subtle brain abnormalities, automating lesion detection and integrating seamlessly into clinical workflows.
By improving diagnostic accuracy, supporting surgical planning, and enabling personalised treatment, it enhances patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency. We aim to collaborate with hospitals, imaging centres, and industry partners to accelerate adoption and expand access to data-driven neurological care.
Our Technology
Our software is a cloud-based neuroimaging platform that detects and visualises subtle brain abnormalities using advanced computational models.
Originally developed in epilepsy, the technology is grounded in extensive neuroimaging research and designed to be adaptable across multiple neurological conditions.
By integrating structural and diffusion MRI, analysing both grey and white matter, and applying normative modeling, we highlight brain regions that deviate from healthy population pattern, particularly where conventional imaging may fall short.
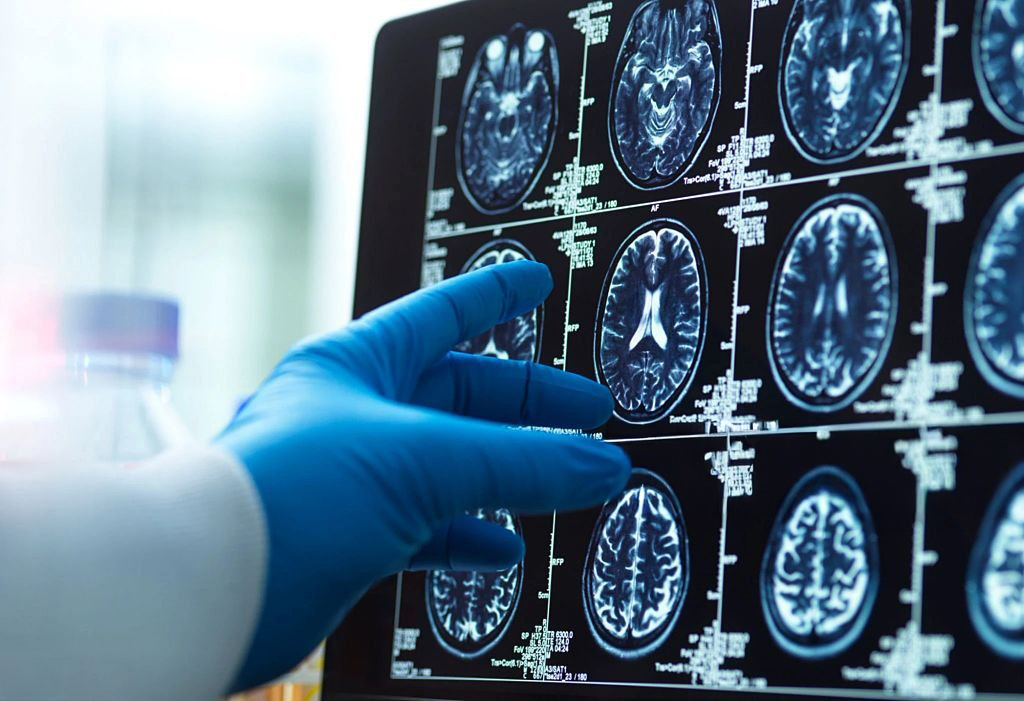
The Problem
About 50 million people worldwide live with epilepsy, and 30% are drug-resistant and could benefit from better diagnostic imaging.
Epilepsy surgery is one of the most effective treatments we have for drug-resistant epilepsy, but long-term seizure freedom still plateaus at ~50% EpiVis uses automated, quantitative, whole-brain MRI analysis to improve detection, reduce missed abnormalities, avoid repeat scans, and shorten treatment delays.
For patients, this leads to higher seizure-freedom rates, faster recovery, preserved cognitive function, lower long-term healthcare dependence, and better quality of life and societal participation
Value Proposition
A cloud-based neuroimaging platform that detects subtle brain abnormalities right now focusing on epilepsy by combining structural and diffusion MRI with advanced normative modelling.
It delivers fast, interpretable maps of potential brain abnormalities, reducing diagnostic uncertainty, supporting multidisciplinary decisions, and enabling personalised treatment strategies. Fully automated and scalable, it can integrate seamlessly into clinical workflows, improving patient outcomes while addressing a critical unmet need for objective, data-driven decision support in epilepsy care.

Our Solution
Our software is a cloud-based neuroimaging platform that detects and visualises subtle brain abnormalities using advanced computational models.
Originally developed in epilepsy, the technology is grounded in extensive neuroimaging research and designed to be adaptable across multiple neurological conditions.
By integrating structural and diffusion MRI, analysing both grey and white matter, and applying normative modeling, we highlight brain regions that deviate from healthy population pattern, particularly where conventional imaging may fall short.
Our Evidence
Selected publications supporting this solution:
Seizure freedom after surgical resection of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/epi.18490
Normative brain mapping of interictal intracranial EEG to localize epileptogenic tissue
https://academic.oup.com/brain/article/145/3/939/6514463
Structural Brain Network Abnormalities and the Probability of Seizure Recurrence After Epilepsy Surgery
https://www.neurology.org/doi/full/10.1212/WNL.0000000000011315
Combined impact of gray and superficial white matter abnormalities: Implications for epilepsy surgery
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/epi.18494?af=R
Multimodal integration of magnetic resonance imaging and intracranial electroencephalographic abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy surgery
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41427675/
Seizure freedom after surgical resection of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/epi.18490
Normative brain mapping of interictal intracranial EEG to localize epileptogenic tissue
https://academic.oup.com/brain/article/145/3/939/6514463
Structural Brain Network Abnormalities and the Probability of Seizure Recurrence After Epilepsy Surgery
https://www.neurology.org/doi/full/10.1212/WNL.0000000000011315
Combined impact of gray and superficial white matter abnormalities: Implications for epilepsy surgery
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/epi.18494?af=R
Multimodal integration of magnetic resonance imaging and intracranial electroencephalographic abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy surgery
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41427675/
Multimodal integration of magnetic resonance imaging and intracranial electroencephalographic abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy surgery
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41427675/
Structural Brain Network Abnormalities and the Probability of Seizure Recurrence After Epilepsy Surgery
https://www.neurology.org/doi/full/10.1212/WNL.0000000000011315
Early deviation from normal structural connectivity: A novel intrinsic severity score for mild TBI
https://www.neurology.org/doi/full/10.1212/WNL.0000000000008902
White matter microstructural properties in bipolar disorder in relationship to the spatial distribution of lithium in the brain
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165032719303040
Publications
https://www.cnnp-lab.com/publications
Our team
Csaba Kozma
Postdoctoral researcher & EpiVis co-developer
Dr. Sarah Smith
TTO Business Dev Manager driving IP and spin-outs
Dai Hayward
Ex-CEO Micropore Technologies
Prof. Peter Taylor
UKRI Future Leaders Fellow & co-lead of a neurology lab
Your Feedback
We need your feedback to continually develop our neuroimaging platform. Please complete the questionnaires below.




